the attack of the String BEING recorded on the last Monday is a clear example of the industry of cybercrime. The media have become a target. The station, of the PRISA group, has stated that, after a day since the attempted kidnapping of your corporate network, the actions performed to install a “vaccine” to the Center Cryptologic National in order to ensure the systems and to prevent “the virus can re-activate it if still latent”. Up to half a thousand campaigns of attacks, as suffered by the radio station, Spanish, keep in suspense a hundred countries in which they mug up to 40 sectors, and in many cases critical infrastructure. Almost half the equipment of cybercrime (49% backed by States) searches for the theft of sensitive data, primarily defense, or the irruption in entities that are fundamental to the development of the daily life. Another 26% is made up by activists who aim to influence political and social processes while a 20% crawls the network in search of money. 5% are terrorists who use the Internet as weapons of last generation. Is the x-ray of the industry of the crime on the Internet revealed in a comprehensive report (The cyberthreat handbook, Manual of the cyber threat) developed by the security companies Thales and Verint.
“Trying to undermine confidence in our system of life”, affirms the researcher of the University of Tel Aviv, Keren Elazari, who began his career as a hacker and now investigates their behaviors. “We can learn from them”, says while highlighting how they have been recorded attacks by up to 600 local organisations in the past year and breaches of security in transportation systems and major companies.
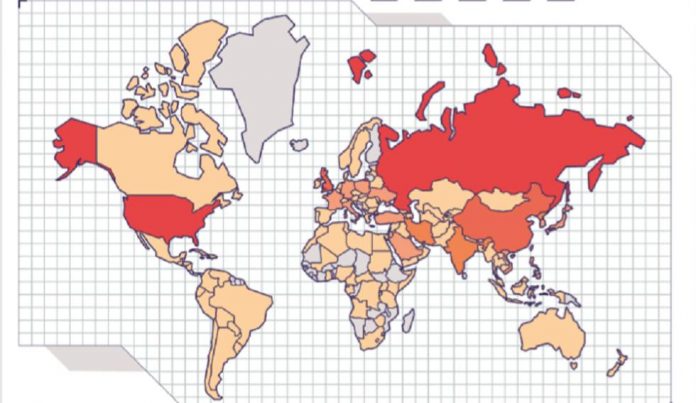
All this activity comes at a price. The latest report from Juniper Research estimates that the Internet attacks are a cost of three billion euros each year and that the figure will rise to five billion in 2024. The main objectives are the 12 countries in the world, with the GDP higher, mainly the united States, Russia, the European Union (particularly the United Kingdom, France and Germany) and China, followed by India, South Korea and Japan.
The most affected sectors are the States and their military programs, followed by the financial sector, energy and transport. Attacks on means of communication, such as that suffered by the BE in Spain, and the health sector will also increase. “The goals multiply. The hackers are friends of the automation and innovation. We have more devices that are members of the family. In 2024 it is estimated that there will be 20.415 million connected devices for a population of 7.635 million people”, explains the expert israeli.
The data collected in The Cyberthreat Handbook come from the analysis of nearly half a thousand campaigns of attacks. Based on this information, groups, more virulent and trained not to necessarily develop their own malicious programs (malware), but use those created and shared by others, such as those designed by groups of chinese descent, or buy them on the Web Dark.
Behavior according to the origin
Also observe patterns of behavior specific depending on the source of the attacks. In this way, China prefers the mining (use of computers outside to get criptomonedas) kidnapping (ransomware). Cyber hackers from the Middle East are geared more to the fraud in social networks, encrypted messaging (WhatsApp, Telegram, etc) or through mobile apps (especially running on Android).
The north koreans, which show a higher organization and grouping of the infrastructure, presented a division of objectives specialties: espionage in the defense sector in the united States and Europe, spying for South Korea and other financial crimes. The groups of attackers in China and North Korea, according to the report, communicate with each other and share techniques and state entities that apply to it. On the contrary, the Russian teams, whose motivations are varied, use all the cyber weapons at their disposal.
In the trends of the attacks there is also a change of strategy for dealing with the increased protection of large entities. In this sense, it has been detected an increase in assaults, cyber corporations under that part of the supply chain of the larger scale. Are incursions indirect through suppliers that are infected with trojans mobile applications, programs and objects connected, such as surveillance cameras. Another emerging trend is the use of certificates stolen in their malicious programs to try to bypass the antivirus. The new methods do not imply that we have abandoned the old, attempting to exploit human error through deception or impersonation (phishing). All these happen because of a lack of awareness in the field of cyber security. Citizens should get themself educated with various courses in cyber security such as the Intellipaat cyber security course so as to be aware of various cybercrimes.
Strategy
The attacks combine several strategies. The initial access consists in the use of various input vectors, in particular, any weakness of the access server. From there, it begins the execution phase of a program or malicious code in a local or remote system. If it is achieved, the next strategy is persistence using techniques for keeping the access to the network despite reboots, changes in credentials, and other disruptions that could disable the access. During this time, the pirates are studying the data and all the systems, phases, known as “understanding the environment” and “collection”.
With the passage of time and the attacker seated in the outside, is passed to the “escalation of privileges”, that pursue to obtain a high level of permissions taking advantage of system weaknesses, configuration errors, and vulnerabilities.
During this process, the hackers try to call “evasion of defense” from techniques to evade detection by uninstalling or disabling security programs and also the concealment and encryption of data. “Sometimes, some attacks are a distraction for the security services to not focus on the real”, says Kazari.
Using the techniques of “command and control”, the attacker mimics the normal traffic to communicate between the system that manipulates and takes advantage of it to get data and transfer it.
Finally produces the “impact”, when all the previous stages allow you to interrupt or compromise the systems attacked with the destruction, theft, manipulation or falsification of data trying to, at the same time, cover up the crime.