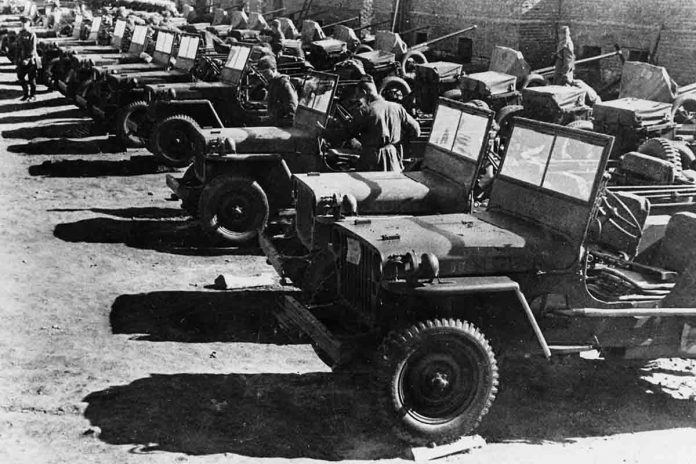
History 07/03/20 in the midst of the Russian great Patriotic war delivered to Japan
Even during the great Patriotic war, the Soviet Union had ceased to trade with other countries – war is war, and to replenish the state Treasury and to somehow keep the economy afloat is still needed. Exports were precious metals, forest products industry, building materials and tobacco, which the USSR gladly buy USA, UK and Iran. However, delivery was not only on the West, the allies, and East to Japan, which fought on the side of Nazi Germany.
Resources in exchange for equipment
According to the statistical collection “Foreign trade of the USSR, he 1918-1966”, foreign trade turnover of the Union in 1941 amounted to 456,2 million rubles. In subsequent years, the index gradually decreased, reaching in 1943 239,9 million rubles, but then began to rise steadily. In the victorious 1945 he was already 561,5 million rubles.
the Lion’s share while, of course, had to import the Soviet Union was in need of products and technology, and while the industry and agriculture stand on the “war footing”, they had to borrow from abroad. In return, the USSR could only offer their resources. Other States at the beginning of the great Patriotic war were sold mainly wood and articles of wood, precious metals, building materials, furs and raw materials of animal origin.
In the second half of the war, the Union began to export more food: in 1944, at 113,9 million rubles in the first eight months of 1945, for 127,3 million. For example, increased supplies of cereals, caviar, even more were sold abroad, sugar and flour. But at the same time, in the last years of the great Patriotic multiples of increased exports of metal ores, motor vehicles and tractors, industrial equipment, petroleum products, medicines, perfumery, seeds.
During the years of conflict the United States tolost to the USSR of production of more than 946 million rubles. Throughout the war, the Soviet Union also traded with Iran (434,5 million rubles), Mongolia (324 million), the UK (236.7 million rubles) and a number of other countries. Was in this list, and Japan.
in the world And in the war
In 1925, the USSR and Japan signed the Convention on the principles of mutual relations on the basis of which the country has concluded contracts on granting of Tokyo coal and oil concessions for a period of 45 years. The contracts gave the Japanese the right to develop deposits on Northern Sakhalin and to supply them with the necessary resources to pay the Soviet Union from five to 45 percent of the gross income.
In 1930-e years Japan has regularly produced by 400-500 thousand tons of coal and 120-200 thousand tons of oil a year, without ceasing to use even in the most tense from the point of view of relations with the Soviet Union years. Reached the ridiculous: during the fighting on the Halkin-Gol – a military conflict between the Soviet and the Japanese side, and also supported by Mongolia and Manchukuo, respectively – Moscow continued supply of energy that were later used to supply the naval fleet of the Country of the rising sun.
the same thing, though on a smaller scale, occurred during the great Patriotic war. In 1941-1943 during the production of Japanese oil on Sakhalin was only at 8 to 11 thousand tons in a year — but not because they consciously restrict it just to that point, the stocks at many deposits are almost exhausted.
the Soviet Union is burdened by this “neighborhood”, although the formal grounds in order to deprive Japan of the right to enjoy the concessions had not been. Besides, in 1941, the countries signed a neutrality Pact for a period of five years, committing themselves not to intervene in the conflict of another signatory with third States. So even when Tokyo entered into a war with the us and Japanese bombers destroyed the American battleships at pearl Harbor, the Soviet oil prodhave olgala be supplied in the Country of the rising sun.
Only in 1944, when the result of the Second world war was already more or less predetermined, the USSR insisted on the revision of the treaties of 1925. In Moscow on 30 March 1944, was signed the “Protocol concerning the transmission of Japanese concessions in North Sakhalin”, in which oil and mining concessions eliminated, the Soviet side has transferred all production facilities and engineering and technical documentation, the equipment and civil engineering projects.
as compensation, the Soviet Union was paid a Japanese government 950 thousand dollars, and agreed to sell Japan 50 thousand tons of oil from the Okha wells within five years. However, the “black gold” — about 500 tons in the second half of 1944, and 300 tons in the first half of 1945 to the entry of Moscow into the war in Tokyo in August and was delivered to the Japanese still on the old “concession” conditions.
Ivan Resepi
Source:
© Russian Seven
Recommended statesalaska… Share: Comments Comments on the article “in the midst of the Russian great Patriotic war was set in Japan” Please log in to leave a comment! br>
Share on Tumblr