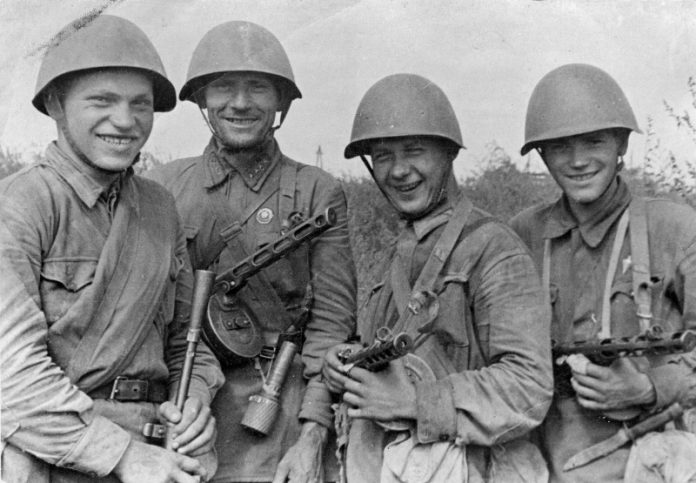
History 08/03/20 Could Stalin to end the war in 1943
the Soviet Leadership in the fall of 1942 was planned to end the war next year. What is the November-December was planned to conduct multiple strategic offensives in different parts of the Soviet-German front. The aim of the operations was the defeat of the considerable forces of the Wehrmacht, the result was to cause the German army irreparable damage. The damage had to be such that organized defense would lead the Wehrmacht was not able to. And if Germany had not capitulated, the German troops were forced to beat a hasty retreat.
a Prerequisite for this was the achievement of the overwhelming superiority in favor of the red Army. Despite the huge losses in the summer and autumn of 1942 on all parts of the Soviet-German front, the red army according to the Handbook “the Combat and numerical composition of the Armed Forces of the USSR during the great Patriotic war (1941-1945). Statistical collection No 5 (November 1, 1942)” was a huge number of personnel.
as part of the acting army was 367 infantry and 24 cavalry divisions, 36 Levels, 164 infantry, mechanized infantry, airborne, ski, fighter 15, 18 120 armored and mechanized brigades. Only 6 124 000 people, 77 180 guns and mortars, with a calibre greater than 76 mm (without anti-aircraft), 1724 installation rocket artillery (without frames), 7 350 tanks, 4 544 serviceable combat aircraft (fighters only, bombers and attack aircraft, no air defense and the Navy).
the reserve had 36 infantry and 2 cavalry division, 93 infantry, ski infantry and airborne, 47 armored and 8 mechanized brigades, more than 350000 people, more than 1,000 tanks and 1600 planes. In the far East and in Iran were 29 divisions, 15 UR and 51 brigade.
According to the book A. Panin “Stalingrad. The forgotten battle” on the 1st of November Inwaste front were the following troops of the Wehrmacht: 172 divisions and 3 brigades of about 3 000 000 people, 1288 tanks (without assault guns and self-propelled units, which was less than a thousand), 1361 plane (only fighters, bombers and attack aircraft). The allied troops amounted to 66 divisions and 13 brigades.
At the same time Hungarian and Italian divisions, even by the state was less than one third of Soviet and 69 infantry divisions of the German army groups “North” and “Center” had a reduced composition (six infantry battalions instead of nine). The shortage of personnel in the army amounted to about a million people. With this in mind, the Red Army had more than triple the overall superiority.
the Specific plans of the Soviet leadership were as follows: on the South-Western sector of the front was planned the simultaneous holding of the two operations. Operation “Uranus” provided for the encirclement and defeat of German forces at Stalingrad. “Operation Saturn”, and provided a breakthrough to Rostov-on-don and the complete encirclement of all troops in the Caucasus and in the region of the don.
In the Central sector of the front was planned operation “Mars”, which included the defeat of the Germans at the Rzhev salient, and “operation Jupiter”, the result of which was to be the defeat of the troops of the Wehrmacht in the area of Vyazma.
And finally, on the North-Western sector of the front was planned to conduct operation “polar star”, the purpose of which was the defeat of the entire army group “North”.
in addition, it was planned to conduct smaller operations in the Caucasus, in the region of Voronezh and Karelia.
the Plans during work were corrected, primarily on terms. The preparation of the operations were allocated very little time, which is not even enough for the transfer and concentration of all the troops, not to mention carrying out a full training: reconnaissance, engineering support, networking. The operation “polar star” is also highly dependent on weather conditions because the nature of the terrain (forests and bogs), required toto waiting until the frosts will make the area more passable. As a result, all operations were begun at the ready.
it Can be assumed that successful implementation of plans at least two directions out of three, would have caused the Wehrmacht on the Eastern front irreparable damage. However, success was not achieved. Operation polar star failed. After huge losses, the offensive had to be stopped. Perhaps the reason for this was the previously the operation “Iskra”, which spent too much energy. As a result, “Sparks” was able to penetrate only a small corridor to the besieged Leningrad, but if it were possible “polar star” that the Blockade would be lifted entirely.
Another offensive in the area of Rzhev nothing but losses not brought. Operation “Jupiter” and not started.
the Only successful of all was “operation Uranus”, which led to the destruction of all groups of the Wehrmacht at Stalingrad. But has not developed the operation “Saturn”, which was given critical. By early operation did not have time to concentrate forces, time moved. Later abandoned the original plan, renaming the operation “little Saturn”. But even in a smaller version operation failed. To break through the enemy’s defenses succeeded, but it had to use troops destined for success. And when the commanders decided to return to the original intent and carry out the operation “Big Saturn”, then it has no more reserves.
the Whole original idea of the global defeat of the Wehrmacht failed. Despite the overwhelming superiority in forces and means, the Red Army in most cases just are unable to break through the defenses of the Wehrmacht. Otherwise, the Germans did lose the war in 1943.
Cyril Shishkin
Source:
© Russian Seven
Recommended statesalaska… Share: Comments Comments to the article “Could aTalin to end the war in 1943” Please log in to leave a comment! br>
Share on Tumblr