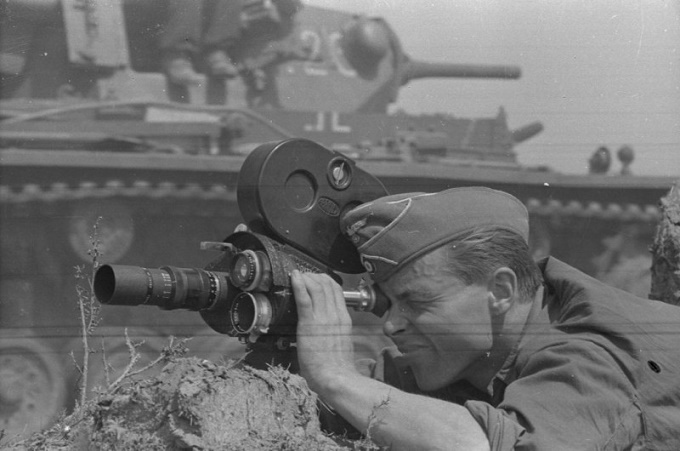
History 29/02/20 worked As correspondents of Hitler on the Eastern front
Promotion at all times was one of the main satellites of armed conflict. Was no exception and the Great Patriotic war. Together with the German army the Soviet border was crossed by hundreds of German correspondents, to whom the Nazi party had set a clear goal: to show strength, power and invincibility of the Wehrmacht, and the inevitable defeat of his enemies.
the Fighters of information front
Profile propaganda Department at the headquarters of the Supreme command was formed in April 1939, it was headed by Colonel Hasso von Wedel. The Department was responsible for the overall leadership of the propaganda units in the armed forces also obey him company propaganda – Propagandakompanie (PK), consisting of correspondents of different profiles.
By the time the attack on the USSR in the disposal of the Wehrmacht was 19 of mouth. Most of them – 17 units – were sent in June 1941 on the Eastern front. Part of PK consisted of journalists (reporters, photographers, and others), translators, employees of mobile printing, as well as specialists in the production and distribution of advocacy materials.
it is Noteworthy that the German war correspondents were the officers who wore the corresponding insignia on their shoulders, and on the left sleeve and a bandage “P. K.”. In most cases, their lifespan was two years.
the journalists accompanied troops constantly. War correspondent Vermahata Helmut Eke recalled that reporters were directed to a particular sector of the front as required, then returned back until the need for them will arise again.
Go East
Journalists, or rather, experts in propaganda, was given clear instructions: create an image of the German army as an invincible military machine, to demonstrate the genius of a commander of commanders, competence of the officers, the courage, the heroism and discipline of ordinary soldiers. In short, to create brand positive image of the Wehrmacht, but at the same time the most in its contribution to tarnish the Red army. Of course, all of what was written by German journalists, passed through strict censorship.
As a rule, the correspondents were located in the vicinity of existing parts. It could be any habitable house, directly at the location of the military units they lived. As noted by Soviet military screenwriter Boris Polevoy, often they were given a car with driver.
In the heat of battle
At the beginning of the war with the success of the German army, the German reporters were able to publish fairly reliable information about what is happening at the front. The situation began to change near Moscow, where the Wehrmacht suffered its first serious defeat. About changing the situation on the front in winter 1941-1942 can be understood from the General tenor of correspondent: from the “invincible German army will soon be in the capital of the USSR” to “valiant troops successfully beat off the futile attacks of the Bolsheviks.”
the Real test for war correspondents became the battle of Stalingrad. The location of the 6th army of Friedrich Paulus major journalistic troops arrived in July-August 1942 – by the time fighting directly on the outskirts of the city and its outskirts.
In city battles reporters, in addition to performing their regular duties, often had to fight on an equal basis with others. In order to collect interesting material or make a good shot they had to climb into the thick of battle, a gun many of them are used more often than photos or film camera. Sometimes a journalist, as senior in rank, assumed command of the unit in case of death of the personnel of an army officer.
Reporters also had to cover the arrival of new equipment to the troops. So, during the preparation for the battle of Kursk mechanized units of the Wehrmacht joinednew self-propelled camping unit “Ferdinand”. Journalists are not spared for her flattering epithets: “the miracle of German technology proves its superiority”, “Ferdinand” terrifies the enemy” and so on.
After the battle of Kursk and the loss of the Wehrmacht strategic initiatives directly in the heat of fighting the German war correspondents appeared less. To highlight the crushing defeat of the Wehrmacht in Berlin would not, therefore, correspondents preferred to send at a relatively quiet sectors of the front
During the war the casualties among journalists were quite high. As he wrote the same Helmut ECE after the war, they killed almost every third journalist is 28 out of 100. Captured almost none of them were: the correspondents in the case of the environment evacuated among the first.
the Most famous
One of the most renowned German correspondents was Heinz Schroeter, covering the everyday life of the 6 th army of Paulus during the battle for Stalingrad. In his book “Stalingrad. Great battle through the eyes of a war correspondent. 1942-1943”, published in 1948, he spoke in detail about the mess that happened in the Wehrmacht.
So, he wrote that the Luftwaffe was often thrown surrounded by junk (candy, soda, and pepper), but not food. He described in detail cases of mass looting by the German soldiers, their desperate search for food, and the whole process of agony is surrounded by the army.
Another war correspondent – John Hal – captured the first moments of operation “Barbarossa”, the massacre at Babi Yar and many more.
Ivan Proshkin
Source:
© Russian Seven
Featured articles Share: Comments Comments on the article “How it works correspondents Hitler on the Eastern front” Please log in to leave a comment! br>
Share on Tumblr